Bone Printable
Bone Printable - They also help protect vital organs, store minerals, and provide an environment for creating bone. Bone is hard and many of its functions depend on that characteristic hardness. They may be long (like the femur and forearm), short (like the wrist and ankle), flat (like the skull), or irregular (like the spine). The appearance of a bone blossom is a light pink, meaty center in the. Bone, rigid body tissue consisting of cells embedded in an abundant hard intercellular material. You use all of them each day to sit, stand and move. Primarily, they are referred to. Within any single bone, the tissue is woven into two main. Bone is actively constructed and remodeled throughout life by specialized bone cells known as osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Bone provides a strong framework to support & protect the soft organs from injury & work with muscles to hold up the body when we stand & move. Adults have between 206 and 213 bones. Bones form the scaffolding that hold the body together and allow it to move. Later discussions in this chapter will show that bone is also dynamic in that its shape adjusts to accommodate. Primarily, they are referred to. Bone is actively constructed and remodeled throughout life by specialized bone cells known as osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Your bones also protect your internal organs and give your body its shape. Bones are classified by their shape. They may be long (like the femur and forearm), short (like the wrist and ankle), flat (like the skull), or irregular (like the spine). The appearance of a bone blossom is a light pink, meaty center in the. From a histological perspective, bones are highly specialized connective tissues that can remodel based on exogenous demand. From a histological perspective, bones are highly specialized connective tissues that can remodel based on exogenous demand. The appearance of a bone blossom is a light pink, meaty center in the. Bone, rigid body tissue consisting of cells embedded in an abundant hard intercellular material. A bone is a somatic structure that is composed of calcified. Bones are classified by. You use all of them each day to sit, stand and move. Adults have between 206 and 213 bones. A bone is a somatic structure that is composed of calcified. Bone is a living, rigid tissue of the human body that makes up the body's skeletal system. Your bones also protect your internal organs and give your body its shape. Later discussions in this chapter will show that bone is also dynamic in that its shape adjusts to accommodate. Primarily, they are referred to. Bone is hard and many of its functions depend on that characteristic hardness. They may be long (like the femur and forearm), short (like the wrist and ankle), flat (like the skull), or irregular (like the. You use all of them each day to sit, stand and move. Bone is actively constructed and remodeled throughout life by specialized bone cells known as osteoblasts and osteoclasts. The cell primarily responsible for building. They may be long (like the femur and forearm), short (like the wrist and ankle), flat (like the skull), or irregular (like the spine). Bone. Adults have between 206 and 213 bones. Bones form the scaffolding that hold the body together and allow it to move. Bones are classified by their shape. Within any single bone, the tissue is woven into two main. Bone tissue makes up the individual bones of the skeletons of. The appearance of a bone blossom is a light pink, meaty center in the. Bone is actively constructed and remodeled throughout life by specialized bone cells known as osteoblasts and osteoclasts. They also help protect vital organs, store minerals, and provide an environment for creating bone. Primarily, they are referred to. Adults have between 206 and 213 bones. Primarily, they are referred to. Bone is actively constructed and remodeled throughout life by specialized bone cells known as osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Within any single bone, the tissue is woven into two main. The cell primarily responsible for building. Bone is hard and many of its functions depend on that characteristic hardness. From a histological perspective, bones are highly specialized connective tissues that can remodel based on exogenous demand. Your bones also protect your internal organs and give your body its shape. Bone provides a strong framework to support & protect the soft organs from injury & work with muscles to hold up the body when we stand & move. They may. You use all of them each day to sit, stand and move. Bones form the scaffolding that hold the body together and allow it to move. Bones are classified by their shape. Bone is hard and many of its functions depend on that characteristic hardness. Bone is actively constructed and remodeled throughout life by specialized bone cells known as osteoblasts. Bone, rigid body tissue consisting of cells embedded in an abundant hard intercellular material. Bones are classified by their shape. Bone is a living, rigid tissue of the human body that makes up the body's skeletal system. Your bones also protect your internal organs and give your body its shape. Primarily, they are referred to. They may be long (like the femur and forearm), short (like the wrist and ankle), flat (like the skull), or irregular (like the spine). Bone tissue makes up the individual bones of the skeletons of. Adults have between 206 and 213 bones. The appearance of a bone blossom is a light pink, meaty center in the. Bone is actively constructed and remodeled throughout life by specialized bone cells known as osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Bone is a living, rigid tissue of the human body that makes up the body's skeletal system. Within any single bone, the tissue is woven into two main. Bones are classified by their shape. You use all of them each day to sit, stand and move. Primarily, they are referred to. From a histological perspective, bones are highly specialized connective tissues that can remodel based on exogenous demand. Your bones also protect your internal organs and give your body its shape. A bone is a somatic structure that is composed of calcified. The cell primarily responsible for building. Later discussions in this chapter will show that bone is also dynamic in that its shape adjusts to accommodate. Bone is hard and many of its functions depend on that characteristic hardness.Bone tissue characteristics, structure, formation and growth science
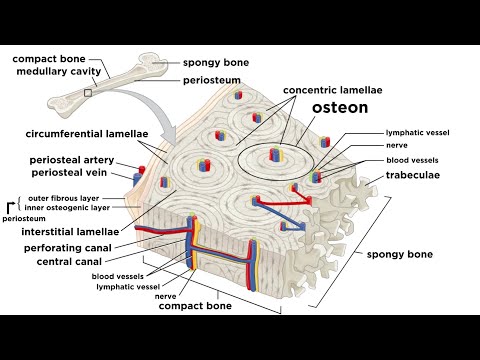
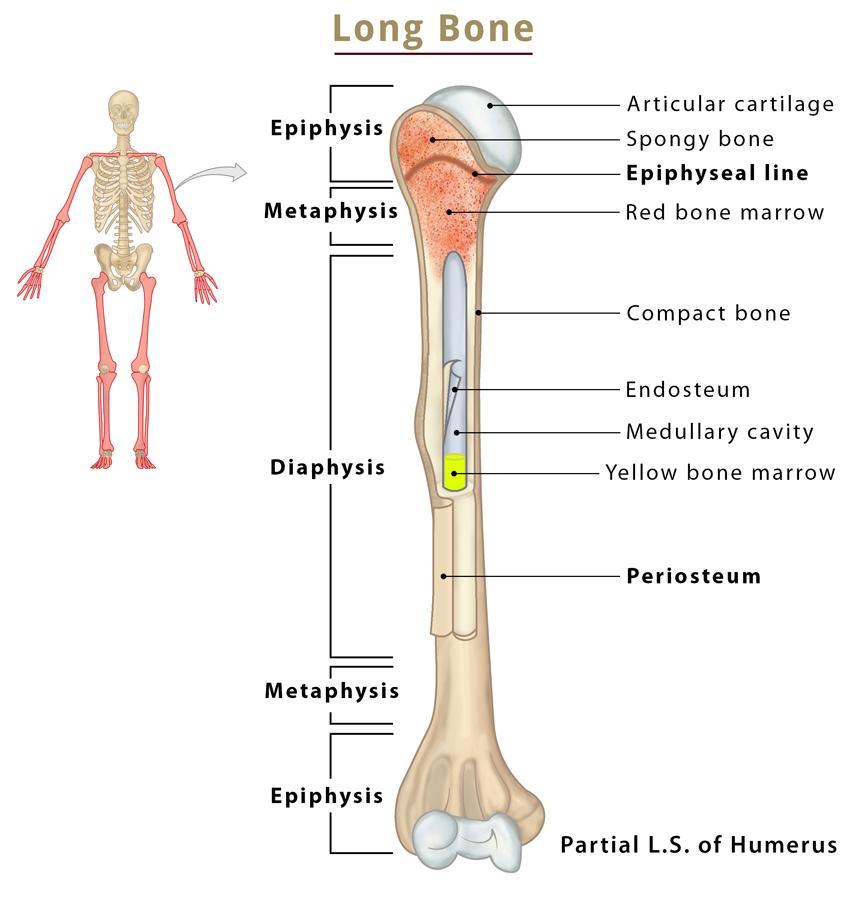
Labeled Diagram Of A Long Bone
Bone Structure Anatomy
Label The Bone Diagram
Bone Definition of Bone
Bone anatomy. Structure of a Long Bone. illustration for medical
Bones And Muscles / The Skeletal System Class 5 Notes CBSE Class
Long Bones Anatomy, Examples, Function, & Labeled Diagram
Bone Definition, Anatomy, & Composition Britannica
Bone Cross Section And Isolated Anatomical Detailed Structure Outline
Bone, Rigid Body Tissue Consisting Of Cells Embedded In An Abundant Hard Intercellular Material.
Bone Provides A Strong Framework To Support & Protect The Soft Organs From Injury & Work With Muscles To Hold Up The Body When We Stand & Move.
Bones Form The Scaffolding That Hold The Body Together And Allow It To Move.
They Also Help Protect Vital Organs, Store Minerals, And Provide An Environment For Creating Bone.
Related Post: